Water Velocity
The river turbine converts the kinetic energy of the river current into electricity. Its energy production
depends on the water velocity. So, the stronger the current, the more electricity the river turbine will produce.
The velocity of the river is usually expressed in terms of meters per second (m/s). One meter per second is the equivalent of 2 knots.
The speed can be measured using appropriate tools such as a current meter.
Here are some examples of river velocities which represents the ideal speed for the use of the river turbine.
Energy production
The process of power production goes as follows: the river current enables the spinning movement of the turbines
which activates the generator. The energy which ensues is then converted into electricity thanks to the built-in smart converter.
Afterward, the converted energy is forwarded to the batteries by an electric cable. The batteries recharge 24h a day and
from there an inverter transforms the direct current (24-48 V DC) into alternating current (120 V AC) to power electrical devices.
The graph below illustrates the daily production capacity of the river turbine which varies between
4 to 12 kWh/day depending on the water velocity available.
The energy production, accumulated in the battery bank is expressed in kilowatt-hours a day (kWh / day).
ENERGY PRODUCTION ACCORDING TO VELOCITY OF WATER
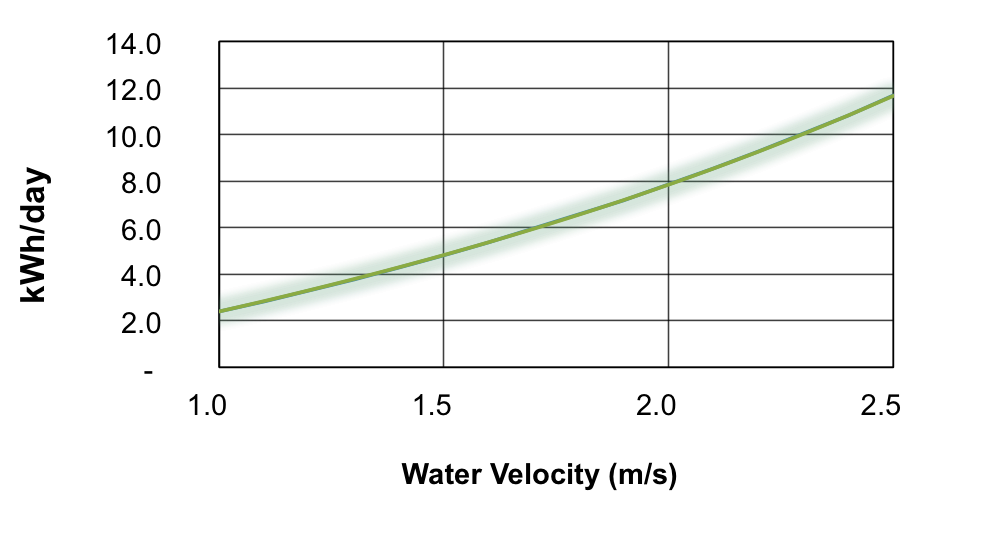
The data of the graph presented below is illustrated in the following chart:
| Water velocity (m/s) | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daily production (kWh/day) | 2,3 | 4,7 | 7,8 | 11,6 |




